The evolution of digital customer interaction has moved far beyond basic chatbots. In 2026, businesses are embracing AI agents that operate like real sales employees—capable of qualifying leads, conducting negotiations, and closing deals autonomously. This shift is accelerating business growth, reducing operational costs, and reshaping how companies deliver personalized customer experiences.
AI agents are no longer simple support tools. They are becoming strategic digital workers, integrated into sales pipelines, customer service, workflows, and revenue operations.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous systems that:
-
perceive customer intent,
-
analyze context in real time,
-
make decisions,
-
and take actions without human intervention.
They combine:
-
Large Language Models (LLMs)
-
Predictive analytics
-
Workflow automation
-
Multi-step reasoning
- CRM data integration
This allows them to behave like mini digital employees—consistent, scalable, and always improving.
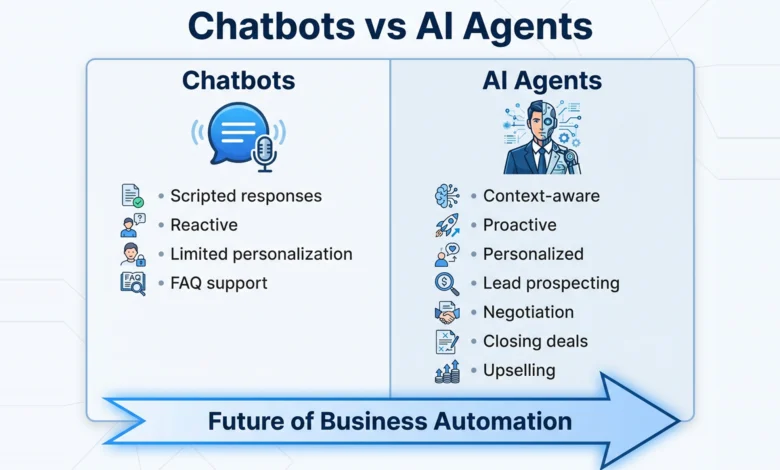
From Chatbots to Intelligent Agents:
1. Chatbots (Past)
-
Scripted
-
Reactive
-
Limited personalization
-
Only respond to predefined questions
2. AI Agents (Present)
-
Proactive
-
Context-aware
-
Data-driven
-
Capable of executing tasks
-
Able to learn from outcomes
Key Evolution
AI agents shifted from simple “answer machines” to decision-making systems that adapt strategies, optimize conversations, and manage business processes.
Why Businesses Are Adopting AI Agents?
-
Scalability: Manage thousands of clients simultaneously.
-
Hyper-Personalization: Tailored recommendations using first-party data.
-
Shorter Sales Cycles: Predictive scoring and automated qualification.
-
Lower Costs: Reduce dependency on large teams.
-
24/7 Global Support: Consistent service across time zones.
- Operational Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks (follow-ups, nurturing, scheduling).
The Rise of the “AI Sales Employee”
Modern AI agents are no longer just answering FAQs—they are taking on full sales responsibilities:
-
Prospecting: Scanning CRM, website behavior, and enriched data.
-
Lead Qualification: Using intent signals, scoring models, and behavioral analysis.
-
Negotiation: Offering dynamic pricing based on customer profile.
-
Closing Deals: Completing contracts, payments, or subscriptions automatically.
-
Upselling & Cross-selling: Recommending relevant products based on patterns.
-
Retention: Re-engaging dormant customers and preventing churn.
This makes AI agents revenue-generating assets, not just support tools.
Real Business Applications
1. E-commerce
-
Cart recovery
-
Personalized bundles
-
1:1 product recommendations
-
AI-driven checkout assistance
2. B2B SaaS
-
Automated demos
-
Lead nurturing sequences
-
Account-based engagement
3. Financial Services
-
Automated onboarding
-
Investment suggestions
– Risk-based profile matching
4. Healthcare
-
Patient pre-screening
-
Appointment workflows
-
Service recommendations
SEO & Content Strategy Transformation
AI agents are changing how people search online. Companies now optimize for:
1. Conversational Search
Queries become longer, natural, and intent-based.
2. Voice Search Optimization
Short, clear, structured answers win.
3. AI-First Content
Content must be:
-
structured,
-
skimmable,
-
data-backed,
-
and optimized for SGE summaries.
Ethical and Operational Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
-
Transparency: Users should know when interacting with AI.
-
Data Privacy: Secure handling of personal and financial information.
-
Bias Reduction: Avoid reinforcing unfair decision patterns.
-
Human-in-the-Loop: AI should enhance—not replace—human oversight.
FAQ:
1. What is an AI agent in business?
An AI agent in business is an autonomous system that analyzes customer intent, makes decisions, and performs tasks like sales, support, and workflow automation without human intervention.
2. How are AI agents different from chatbots?
AI agents are proactive and decision-making, while chatbots are reactive and scripted. Agents can qualify leads, negotiate, and complete tasks; chatbots mainly answer predefined questions.
3. Can AI agents replace human sales employees?
AI agents can handle repetitive sales tasks such as qualification, follow-ups, and recommendations, but they complement—not fully replace—human salespeople who handle complex negotiations.
4. What industries use AI agents the most?
E-commerce, B2B SaaS, finance, healthcare, hospitality, and telecom use AI agents for automation, personalization, and customer engagement.
5. What are the benefits of AI sales agents?
Key benefits include scalability, 24/7 availability, faster sales cycles, personalized recommendations, cost reduction, and improved customer satisfaction.
6. Are AI agents safe to use with customer data?
Yes, if implemented with strong encryption, privacy controls, and compliance (GDPR, SOC2, HIPAA). Human oversight remains essential.
8. Will AI agents shape the future of customer service?
Yes. They provide instant responses, automate workflows, personalize interactions, and reduce wait times—making them central to next-generation customer service operations.
The transition from scripted chatbots to autonomous AI sales employees represents a major milestone in business automation. Companies embracing this evolution gain competitive advantages in scale, personalization, and operational efficiency. The future belongs to businesses that balance automation with human empathy—creating smarter, faster, and more authentic customer experiences.


